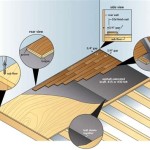
Understanding Flooring Particle Board Thickness
Particleboard, a ubiquitous material in construction and furniture manufacturing, also finds a prominent role in flooring applications. This engineered wood product, composed of wood chips or sawdust bonded with resin, provides a cost-effective and versatile substrate for various flooring types. One crucial factor determining its suitability for flooring is the thickness of the particleboard. This article delves into the significance of particleboard thickness in flooring, explores the factors influencing its selection, and outlines the advantages and disadvantages of different thicknesses.
Factors Influencing Particle Board Thickness Selection
The thickness of particleboard used for flooring is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Several factors influence the appropriate thickness, including the type of flooring to be installed, the subfloor condition, and the expected foot traffic.
Type of Flooring: Different flooring types have varying requirements for particleboard thickness. For example, engineered hardwood flooring often requires a thicker particleboard base for stability, while laminate flooring may be suitable with a thinner substrate. Tile flooring, known for its weight, necessitates a thicker particleboard to prevent sagging or cracking.
Subfloor Condition: Existing subfloor conditions play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate particleboard thickness. If the subfloor is uneven or has significant gaps, a thicker particleboard can help create a more level and stable surface. Conversely, if the subfloor is already in good condition, a thinner particleboard may suffice.
Expected Foot Traffic: The anticipated foot traffic in the area where the flooring will be installed is a critical factor in determining the required particleboard thickness. High-traffic areas, like hallways or kitchens, need a thicker particleboard to withstand extensive wear and tear. Conversely, areas with minimal foot traffic may be suitable with a thinner particleboard.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Thicknesses
The thickness of particleboard directly impacts its performance and suitability for flooring applications. Different thicknesses offer specific advantages and disadvantages, which need to be considered when making the selection.
Thicker Particle Board (1/2" or More)
Advantages: Thicker particleboard offers enhanced stability, greater load-bearing capacity, and better resistance to warping and sagging. It provides a superior base for heavier flooring materials, such as ceramic tiles, and is ideal for high-traffic areas.
Disadvantages: Thicker particleboard can be more expensive than thinner options, and may require more intricate installation techniques. In some instances, it can add significant height to the floor, potentially needing adjustments to existing fixtures or door frames.
Thinner Particle Board (1/4" or Less)
Advantages: Thinner particleboard is more economical and easier to install. It is often suitable for lighter flooring materials, such as laminate or engineered wood flooring, particularly in areas with moderate foot traffic.
Disadvantages: Thinner particleboard may not provide sufficient stability for heavier flooring materials or high-traffic areas. It is more susceptible to warping and sagging, particularly if the subfloor is not adequately prepared.
Considerations for Specific Flooring Types
The choice of particleboard thickness should be tailored to the specific flooring type being installed. Some flooring types have specific recommendations for particleboard thickness to ensure optimum performance and longevity.
Hardwood Flooring
For hardwood flooring, a thicker particleboard substrate is generally recommended, particularly for solid hardwood. At least 1/2-inch thickness is preferred to provide sufficient stability and prevent squeaking or sagging. Engineered hardwood flooring, due to its construction, may tolerate a thinner particleboard, but 1/4-inch thickness is still advisable.
Laminate Flooring
Laminate flooring is typically lighter than hardwood and less demanding on the subfloor. A thinner particleboard, often 1/4-inch, can be sufficient for laminate flooring, but a thicker particleboard can offer greater stability and sound reduction.
Tile Flooring
Tile flooring, being one of the heaviest flooring types, requires a robust subfloor for proper support. A thicker particleboard, often 1/2-inch or more, is recommended for tile installation to prevent cracking and ensure stability. It's essential to consider consulting with a professional tile installer for specific recommendations regarding particleboard thickness for your project.
Selecting the appropriate particleboard thickness is crucial for ensuring the longevity, stability, and performance of your flooring. Carefully considering the factors outlined above will help you make an informed decision for your specific project. Consult with flooring professionals or manufacturers for tailored recommendations based on your needs and project specifics.

Subfloor Options Osb Vs Particle Board New Floors Inc

3 4 In X Ft 8 Particle Board Panel Ru1191248096000000a The Home Depot
Particleboard Structural Flooring Design Manual

Subfloor Options Osb Vs Particle Board New Floors Inc

What Is A Particle Board Are Its Diffe Types

Particle Board As A Flooring Solution

1 4 In X Ft 8 Mdf White Vinyl Side Panel 374964 The Home Depot

Particle Board All You Need To Know

Particle Board Flooring Durable Building Material

Particle Board Wikipedia
Related Posts