Calculating Square Footage for Flooring: A Comprehensive Guide
Accurately calculating the square footage of a floor is a crucial first step in any flooring project, whether it involves installing hardwood, tile, carpet, or laminate. An accurate calculation ensures that enough flooring material is purchased, minimizing waste and preventing costly delays. Underestimating can lead to shortages, requiring additional orders and potentially mismatched dye lots. Overestimating, while less problematic than underestimating, results in unnecessary expenses. This article provides a detailed guide to calculating square footage for flooring, covering various room shapes and accounting for potential waste.
Before embarking on any flooring project, gather the necessary tools. A measuring tape (preferably one that is at least 25 feet long), a pencil, paper (or a digital note-taking device), and a calculator are essential. For more complex shapes, consider using a laser distance measurer for increased accuracy and efficiency. A laser measurer is particularly useful in large rooms or rooms with many obstructions. The accuracy of your measurement directly impacts the accuracy of your square footage calculation, so choosing the right tools is paramount.
Measuring Rectangular and Square Rooms
The simplest room shape to calculate is a rectangle or a square. The formula for area is length multiplied by width: Area = Length × Width. Begin by measuring the length of the room from one wall to the opposite wall, ensuring the tape measure runs in a straight line. Record this measurement in feet. Next, measure the width of the room from one wall to the other, again ensuring the tape measure is straight. Record this measurement in feet. Multiply the length by the width to obtain the square footage. For example, if a room is 12 feet long and 10 feet wide, the square footage is 12 feet × 10 feet = 120 square feet.
If the measurements are taken in inches, divide each measurement by 12 to convert it to feet before multiplying. Alternatively, you can multiply the length and width in inches and then divide the result by 144 (since there are 144 square inches in a square foot) to get the square footage. Consistency in units is critical for accurate calculations. Double-check all measurements and calculations to avoid errors.
Remember to measure the actual floor space, avoiding baseboards or moldings. The baseboards cover the edges of the flooring, so they are not included in the square footage calculation. Account for door thresholds and any built-in obstacles when measuring. These elements may require custom cuts of the flooring material.
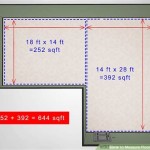
Calculating Square Footage for Irregularly Shaped Rooms
Rooms with irregular shapes, such as L-shaped rooms or rooms with alcoves, require a slightly more complex approach. The key is to divide the room into smaller, more manageable shapes, typically rectangles or squares. Measure each of these smaller shapes individually, calculate their areas, and then add the areas together to find the total square footage.
For example, an L-shaped room can be divided into two rectangles. Measure the length and width of each rectangle. Apply the formula Area = Length × Width to calculate the area of each rectangle. Sum the areas of the two rectangles to determine the total square footage of the L-shaped room. It is useful to sketch the room and label the measurements clearly on the sketch to prevent confusion during the calculation process.
Another common irregular shape is a room with an alcove. Treat the alcove as a separate rectangle and calculate its area. Add the alcove's area to the area of the main section of the room. For rooms with more complex shapes, it might be helpful to use graph paper to create a scaled drawing of the room. This drawing can aid in visualizing the different sections and ensuring accurate measurements.
For rooms with curved walls, approximation is usually necessary. Break the curved section into smaller straight lines and approximate the shape with a series of triangles or rectangles. Measure each of these shapes and add their areas to the total. While this method won't be perfectly accurate, it provides a reasonably close estimate. Alternatively, consult with a flooring professional for rooms with significant curves or unusual shapes. They may have specialized tools or techniques for accurately measuring these spaces.
Accounting for Waste and Pattern Matching
Once the total square footage of the room is calculated, it is essential to account for waste. Waste refers to the extra material needed to accommodate cuts, mistakes, and pattern matching. The amount of waste typically ranges from 5% to 15% of the total square footage, depending on the complexity of the room, the type of flooring, and the installation method.
For simple rectangular rooms with minimal obstacles, a waste factor of 5% to 7% is usually sufficient. This allows for basic cuts and minor errors. For rooms with more complex shapes, such as those with numerous corners, doorways, or alcoves, a higher waste factor of 10% to 12% is recommended. Rooms with angled walls or curved features may require even more waste, potentially up to 15% or higher.
Certain flooring types, particularly those with patterns, require extra waste to ensure proper pattern matching. Patterned carpets, tiles, and some types of wood flooring necessitate careful alignment during installation. The amount of waste needed for pattern matching depends on the complexity of the pattern. Consult the flooring manufacturer's recommendations for the appropriate waste factor for the specific product being used. A complex pattern can easily require 15% or more waste to achieve a visually appealing and seamless result.
To calculate the total amount of flooring needed, multiply the calculated square footage by the waste percentage (expressed as a decimal) and add the result to the original square footage. For example, if the room is 150 square feet and a 10% waste factor is applied, the calculation is as follows: 150 square feet × 0.10 = 15 square feet of waste. Then, add the waste to the original square footage: 150 square feet + 15 square feet = 165 square feet. Therefore, 165 square feet of flooring material should be purchased.
It's generally advisable to err on the side of caution and purchase slightly more material than calculated. This provides a buffer in case of unexpected issues during installation or the need for future repairs. Leftover flooring can be stored for future use or potentially returned to the supplier, depending on their return policy.
When purchasing flooring, carefully review the product specifications. Pay attention to the dimensions of each piece (e.g., tile size, plank width, roll width) and the coverage area per box or unit. This information allows for calculating the number of boxes or units needed to cover the required square footage, including waste. Divide the total square footage required (including waste) by the coverage area per box or unit. Round up to the nearest whole number to ensure sufficient material.
For example, if each box of flooring covers 20 square feet and 165 square feet of flooring is needed, the calculation is 165 square feet / 20 square feet per box = 8.25 boxes. Rounding up to the nearest whole number, 9 boxes of flooring should be purchased. Always double-check the calculations and confirm the quantities with the flooring supplier before making a purchase.
Consulting with a professional flooring installer is highly recommended, especially for complex projects or if you are unsure about any aspect of the measuring and calculation process. A professional can provide accurate measurements, advise on appropriate waste factors, and ensure that the correct amount of flooring is purchased. Their expertise can save time, money, and prevent potential headaches during the installation process.
In summary, accurate measurement, careful calculation, and appropriate allowance for waste are essential for successful flooring projects. By following these guidelines, you can confidently determine the square footage of your floor and ensure that you purchase the correct amount of flooring material.

How To Determine Square Footage For Flooring Vermont Hardwoods

How To Measure Calculate Square Footage Roomsketcher

How To Measure Calculate Square Footage Roomsketcher

How To Calculate Square Footage Of A Room

How To Calculate Square Footage Of A Room

Flooring Cost Calculators For Carpet Tile Vinyl Laminate Wood Floors

How To Measure Calculate Square Footage Roomsketcher

Returns Cancellations

Flooring Calculator Homechisel Simplifying Home Improvement

How To Calculate Square Footage Of A New Floor
Related Posts